Picture this: a doctor completing a long day of patient care in the USA, going home, and yet being too preoccupied to fully relax because he must also complete the paperwork for each visit. Now imagine a place where doctors have to merely speak, and their notes appear instantly, error-free, in the electronic health record.
This is what modern documentation tools promise, but the question is, would you prefer the old medical transcription or rely on cutting-edge speech recognition software? In this blog, we dive into medical transcription vs. speech recognition software exploring how each works, their pros and cons, and how new hybrid models like those offered by ScribeMedics are changing the future of healthcare documentation.
What Is Medical Transcription?
Medical transcription is the conversion of a doctor’s recorded voice notes into written medical reports. Doctors dictate their observations and notes after each patient visit, and trained medical transcriptionists, called healthcare documentation specialists, listen to the recordings of these dictations in context and transcribe the statements appropriately.
They make sure that everything gets included in the patient’s electronic health record (EHR). By using medical transcription software and digital dictation systems, they verify terminology, spellings, and grammar as well as format reports properly.
Accurate medical transcription plays a key role in improving patient care, ensuring proper hospital billing, and maintaining compliance with healthcare standards in the United States of America (USA).
What Is Speech Recognition Software?
Speech recognition software, also known as voice recognition transcription software, employs artificial intelligence and automatic speech recognition (ASR) for converting oral speech to text simultaneously.
The operation of the system is based on ASR models, neural networks, and the technique of natural language processing (NLP) for decoding and making written copies of the spoken words. In a simplified manner, the physician talks, and the corresponding text gets displayed on the monitor instantly.
Current audio-to-text conversion software for transcription is linked with electronic health records (EHRs), thereby enabling physicians to verbally note down patient files instead of having to wait for a transcriptionist. Some of the common examples of this are medical speech recognition software, medical speech-to-text software, and medical voice dictation software.
How Medical Transcription Works
To understand whether medical transcription fits into the debate of medical transcription vs. speech recognition software, you first need to understand its workflow. Unlike automated systems, this process relies on skilled professionals who bring accuracy, judgment, and context to every report.
Here’s how the process works, step by step:
Recording the dictation: The doctor or the healthcare provider records dictations either for patient notes, for summaries of the patients, or for the narration of the procedures using a recorder, a mobile app, or a medical dictation service. The recordings are meant to be complete and take in all aspects of the patient’s visit.
Secure file transfer: The audio file will then be sent by the medical transcriptionist or the transcription company securely via encrypted software. This software is compliant with privacy laws like HIPAA in the United States of America (USA).
Transcription process: An expert healthcare documentation specialist listens to the dictation very carefully, interprets the difficult medical terms, and then, using medical transcription software, types them. They are also required to adhere to hospital-specific templates and formatting rules, so there is no lack of consistency.
Quality review: An additional expert goes through the document, in order, to check for accuracy, proper terminology usage, and compliance with healthcare standards. It is during this human review that we see how medical transcription gets an upper hand over automated speech recognition software in terms of precision.
Final upload: After being verified, the report generated by the physician is uploaded to the patient’s electronic health record (EHR), and it is thus included in the official medical documentation.
The human-oriented transcription process unites medical knowledge with a meticulous focus on detail. It makes sure that every diagnosis, medication, and procedure is recorded correctly, which is a tough task for automated systems. In brief, medical transcription provides the consistency and precision that technology alone cannot fully replicate.
How Speech Recognition Software Works
To understand the main points of speech recognition technology in healthcare, it is essential to know how the whole process works. To put it another way, one could say that this process is the faster and AI-driven side of documentation. As compared to the traditional way of transcribing, the automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems give real-time results to the doctors by converting the spoken words into text.
Now let’s take a look at how the speech recognition flow works stage by stage:
- Speaking the notes: The provider naturally speaks into a microphone, mobile device, or app while or after a consultation with a patient. There is no typing involved; everything is done by voice.
- Converting speech to text: The automatic speech recognition system captures the audio and instantly transforms it into written text. This is the core of speech-to-text transcription software, where algorithms look into voice patterns, tone, and pronunciation.
- Displaying and integrating results: The produced text comes up on the screen in no time at all. Nowadays, medical speech recognition software works closely with electronic health records (EHR) so that the doctor’s notes become a part of the patient’s record automatically.
- Reviewing and editing: Physicians are allowed to review, edit, and finalize the report right then and there. This not only decreases the turnaround time but also facilitates almost instantaneous documentation.
- Learning and improving: The technology behind these tools relies on acoustic models, language models, and deep neural networks. These systems continuously learn from the user’s voice and accent. Over time, they are fine-tuned to recognize medical terminology and improve accuracy, reducing the word error rate (WER) with every use.
Advantages of Medical Transcription
In the debate of medical transcription vs. speech recognition software, one of the most cited advantages for traditional medical transcription is certainly the human element. While machines rely on algorithms and models, trained medical transcriptionists bring real understanding and context to every report.
Here’s a look at why medical transcription still plays an essential role in modern healthcare:
1. High accuracy through human understanding:
A good medical transcriptionist will be able to identify these words/phrases, which even the most advanced speech recognition software may struggle to recognize. Also, unlike machines, humans have a sense of tone and meaning, which can help them steer clear of mistakes that
automated systems could easily make.
2. Strong domain expertise:
Healthcare documentation professionals are skilled in deciphering intricate medical jargon, procedures, and diagnostic terminology. They can understand shorthand, acronyms, and even very poor recordings, something automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems are not capable of.
3. Custom formatting and compliance:
Transcriptionists may also customize their services and accommodate the individual needs of hospitals, insurance companies, and medical specialties. With medical transcription software, they insert format, header, and coding information that conforms to standards regulation and billing guidelines in the United States of America (USA).
4. Built-in quality assurance
The process of transcription consists of several levels of quality control prior to being sent for finalization. By this means, human verification guarantees that the reports contain no errors and are of the same quality. A single mistake in a prescription or diagnosis can lead to serious consequences, so accuracy is non-negotiable.
5. Context and reliability
Human transcriptionists, unlike machines, are aware of the medical context. They can differentiate similar-sounding words according to the context and change the wording for better understanding. This makes medical transcription more trustworthy, particularly in the areas of cardiology, oncology, or radiology, where precision saves lives.
To sum up, medical transcription provides unsurpassed precision and responsibility. It is a guarantee that every medical report is error-free and compliant and is to be merged into the patient’s electronic health record (EHR) without any misunderstandings or assumptions.
Advantages of Speech Recognition Software
In medical transcription vs. speech recognition software, automation “is what makes the voice recorders so superior to other systems.” Physicians no longer have to wait for reports; they can generate notes instantly with their voice.
Below are some of the primary benefits of speech recognition technology in medicine:
1. Real-time documentation
With speech-to-text transcription, doctors can talk into a microphone or an app and watch their notes appear so they don’t have to write them. This is beneficial in minimizing after-hours paperwork and maximizing productivity.
2. Cost savings and efficiency
The moment medical transcription speech recognition software is put into action, there is no need for hiring multiple people for transcribing. Therefore, labor costs at hospitals and clinics would decrease significantly while the rate of documentation would get faster.
3. Seamless integration
Modern medical speech recognition software connects directly with electronic health record (EHR) systems and medical dictation services. Doctors can dictate directly into patient files, streamlining workflow and reducing data entry errors.
4. Scalability for large organizations:
Healthcare systems in the USA that handle thousands of patient encounters daily can scale speech recognition transcription software easily without adding more staff. Cloud-based AI speech recognition platforms process large volumes of data with minimal setup.
5. Flexibility and mobility:
Healthcare professionals can record their notes anywhere, including inside the examination rooms, during telehealth appointments, or when they are on a trip. Documentation is made easy and available with mobile applications and cloud speech recognition services.
6. Continuous improvement with AI
Leading speech recognition tools use advanced techniques like neural networks, ASR models, and natural language processing to get acquainted with a doctor’s vocal styles. Gradually, the systems can become more accurate in distinguishing dialects, medical vocabulary, and even personal pronunciation, thereby decreasing the word error rate (WER) with each use.
In brief, the application of speech recognition technology gives busy doctors the most desired features: speed and convenience. Clinicians can spend more time with patients and less on paperwork; thus, it becomes an important factor in the progress of medical documentation.
Comparing the Two Systems: Medical Transcription vs. Speech Recognition Software
While comparing medical transcription vs. speech recognition software, you’ll need to consider how each system deals with accuracy, speed, cost, and scalability. They both aim to do the same thing make accurate medical documentation,but accomplish it in totally different ways.
Here is their comparison across key performance areas:
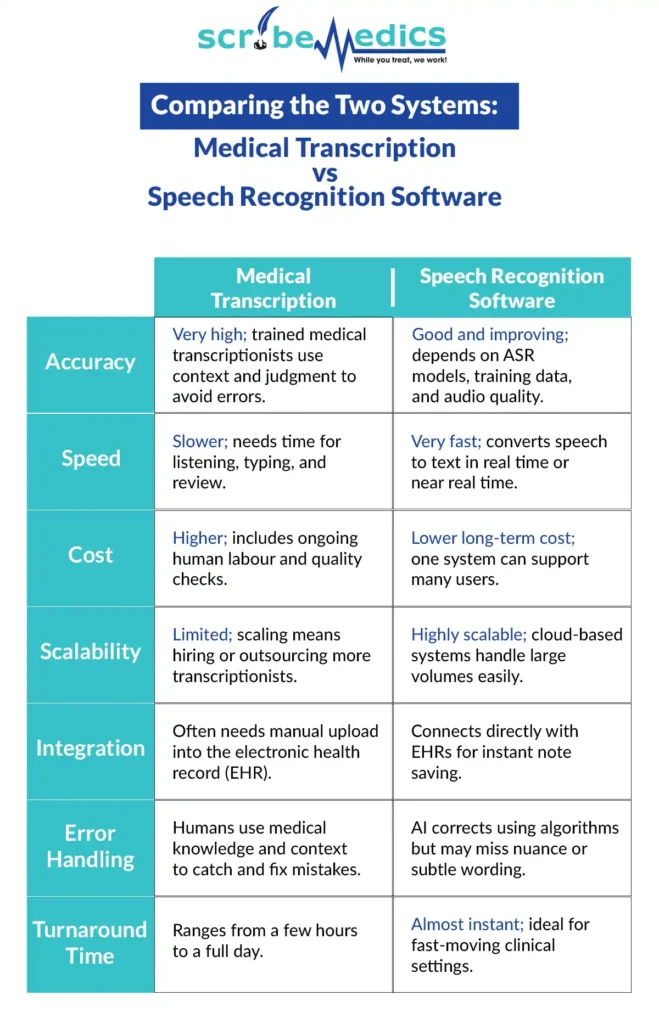
The Science Behind Speech Recognition Software
If you’re wondering why ASR is a game-changer in the world of healthcare, we have to dive into how the technology functions. At the heart of each piece of speech recognition software is a synergy of artificial intelligence, math, and language science working to transform spoken words into accurate text.
In the discussion of medical transcription vs. speech recognition software, this is where technology really thrives: smart systems that can learn and adapt and get better with time.
Here are the key components that make speech recognition technology so powerful:
Acoustic Model: Hearing the Sounds
The acoustic model basically listens to the voice of the user and determines the different sounds that make up the words. It conducts a detailed analysis of pitch, articulation, and intonation, and thereafter it correlates these patterns to the already known phonetic structures. As an illustration, when a physician says “hypertension,” the unique waves corresponding to the word “hypertension” are determined by the model, and the output is connected to the right text.
Language Model: Understanding the Meaning
The language model activates after the sound is identified by the system to forecast which words go together. It employs logic, grammar, and probability in its decision-making process of whether the speaker intends “heart rate” or “hard rate.” Such predictions in healthcare are very important since a minor alteration in wording can lead to a change in medical meaning and patient records.
Neural Networks: Learning Like the Human Brain
The cutting-edge speech recognition artificial intelligence depends on neural networks that portray the way human brains work while processing information. The networks constantly get better and more precise since they are learning from each and every voice input. They are able to handle different accents and pronunciations, not to mention medical jargon, thus increasing their transcription capacity for difficult medical dictations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding Context
Natural language processing (NLP) is a tool that allows the machine to perceive not only the spoken words but also the meaning. For instance, through NLP, it becomes easier for speech-to-text transcription software to detect the context of the medical professional’s speech, whether it is a diagnosis, drug prescription, or procedure. The usage of NLP helps to ensure that the final transcript is medically relevant.
These technologies, when used in combination, make up advanced speech recognition systems that are able to adapt to the user’s voice characteristics, hence reducing the word error rate (WER) with every use. The lower the WER, the higher the accuracy of the transcript.
The introduction of these smart ASR systems in USA hospitals and clinics has changed the documentation process by making it faster and more accurate at the same time. Moreover, the development of neural networks and language models is further closing the gap between human transcription and machine accuracy, hence further altering the way healthcare practitioners deal with medical records.
Common Challenges in the Medical Transcription vs. Speech Recognition Software
Medical transcription and speech recognition software encounter their unique set of problems, despite advocating for accelerated and more precise medical documentation. Knowing these limitations helps healthcare organizations in the United States of America choose the right solution for their needs.
Challenges in Medical Transcription
The old-style medical transcription relies totally on expert professionals, which makes the entire process lengthy. The report must undergo step-by-step transcription, starting from audio recording and going through the entire route of transcription and reviewing, and finally getting uploaded in the electronic health record (EHR). This leads to the longer process of turnaround time, especially where the cohort of transcription is large and dealing with a big bulk of audio files. Operational costs are equally high, as the organizations have to bear the cost of the trained staff or the services of outsourcing. Moreover, the unavailability of the required staff can turn out to be a factor that results in the delays, and manual data entry is an avenue from which small but expensive human errors can occur.
Challenges in Speech Recognition Software
Speech recognition technology is evolving fast, but it is still not free from the problem of accuracy. An automatic speech recognition (ASR) system can incorrectly interpret a complex medical term, acronym, or abbreviation that a human can easily take. Background noise, low-quality microphones, or intermingling dialogs are other reasons that can lower the clarity further. The doctors with thick accents or unusual speech patterns might find the software to be inconsistent in understanding them. If the ASR models are not meticulously fine-tuned, then users end up spending a lot of time going over and making corrections of the errors.
Even the greatest speech recognition software is not a hundred percent right; it works best in silence where the speaker’s voice is clear and the speaker is consistently trained. Ultimately, both systems have certain restrictions, and a majority of hospitals manage to solve these problems by blending human skills with AI-powered transcription tools for undeniably accurate outcomes.
The Hybrid System Advantage
Most hospitals now utilize a hybrid model of speech recognition software and medical transcription services to speed up the process even more, however. In this configuration, the ASR system promptly converts a doctor’s voice into text, and a medical transcriptionist edits the document for precision and readability. This saves time, reduces the costs, and also ensures high-quality documentation. “Human plus AI” companies like ScribeMedics apply this method, trading speed for precision. Through a combination of technology and human expertise, USA health care organizations are efficient without sacrificing patient safety or report accuracy.
Conclusion: The Perfect Balance Between Human and AI
In the current healthcare landscape, the use of medical transcription and speech recognition software is both indispensable and widespread. Each of them brings different advantages that support the doctors in giving more attention to the patients and less to the paperwork.
Human medical transcriptionists offer extraordinary accuracy, taking context and detail into account, while AI voice recognition gives the speed of the documentation and its automation in real time. The combination gives a strong and still trustworthy system that can handle the documentation in a smarter way.
Digitalization of healthcare in the USA continues to advance, while at the same time more and more providers are switching over to the hybrid ASR model where automatic speech recognition (ASR) does not replace but rather supports human expertise.
No matter if you choose traditional transcription, AI-driven speech-to-text transcription, or a hybrid model, the purpose is still straightforward: to relieve the doctor’s burden, to save time, and to offer the patient better treatment through accurate and efficient medical documentation.
Frequently Asked Question
The important distinction between transcription and speech recognition refers to their treatment of audio. Medical transcription relies on human typists who, after listening to the recordings, grasp the medical context and then write the reports accurately. On the other hand, speech recognition systems employ automatic speech recognition (ASR) combined with neural networks to do the job of turning what is said into writing right away. Even though transcription provides the highest accuracy through the human decision, on the other hand, speech recognition technology gives faster results with the whole process being automated. The use of both in the healthcare sector entails a situation in which humans make sure that context and clarity are retained, whereas machines offer the advantages of speed and scalability. The practice of combining both in the USA is widespread among hospitals in order to get more benefits in terms of efficiency.
Speech recognition technology plays a major role in modern medical transcription by improving documentation speed and reducing manual effort. Using AI speech recognition and ASR models, the system converts a doctor’s voice into text automatically. This allows clinicians to document patient encounters in real time, saving hours of typing. The transcribed draft can then be reviewed by a medical transcriptionist for accuracy. This “human plus AI” model ensures fast, error-free records in electronic health records (EHRs). In the United States of America (USA), many healthcare facilities use this combination to lower costs, reduce turnaround time, and enhance patient care efficiency.
There are two main types of speech recognition systems: speaker-dependent and speaker-independent. Speaker-dependent speech recognition software learns a single user’s voice and becomes more accurate as it adapts to that person’s accent, speed, and tone. It’s often used in medical speech recognition software, where doctors use speech-to-text transcription for their reports. On the other hand, speaker-independent systems can understand anyone’s voice without prior training, making them ideal for call centers or general-purpose applications. Both types rely on automatic speech recognition (ASR), neural networks, and language models to accurately convert spoken words into text across different devices and healthcare systems.
Speech recognition software is a digital instrument that, with the help of the ASR (automatic speech recognition) technology, transforms spoken words into written text. It understands speech patterns and medical vocabulary by means of acoustic models, language models, and neural networks. The medical speech recognition software in the healthcare sector has brought about a large reduction in the time doctors take to make notes, as they can now dictate their words straight into the EHRs (Electronic Health Records) rather than typing them. The software gets more accurate as it gets used to each individual’s voice and accent. To the end of increasing productivity, the manual workload reduction, and the more rapid, reliable medical documentation, many hospitals in the USA are employing speech recognition transcription software.
Speech recognition software is a digital instrument that, with the help of the ASR (automatic speech recognition) technology, transforms spoken words into written text. It understands speech patterns and medical vocabulary by means of acoustic models, language models, and neural networks. The medical speech recognition software in the healthcare sector has brought about a large reduction in the time doctors take to make notes, as they can now dictate their words straight into the EHRs (Electronic Health Records) rather than typing them. The software gets more accurate as it gets used to each individual’s voice and accent. To the end of increasing productivity, the manual workload reduction, and the more rapid, reliable medical documentation, many hospitals in the USA are employing speech recognition transcription software.
The progress made by speech recognition software in comprehending medical terminologies has been exceptional, yet its dependability still relies on the proper training of the ASR models. The anticipated accuracy level is reached when the medical speech recognition software, specifically made for the healthcare sector, identifies difficult pronounciations of medical terms, drug names, and operations. For such learning, it employs techniques such as deep learning and natural language understanding (NLU) to detect the sounds made by the different phonemes and thus minimize the word error rate (WER). Nevertheless, if the surrounding area is full of noise or the person talking has a very marked accent, then the accuracy will definitely go down. This is the reason why in most American hospitals a combination of fully automated speech recognition with human medical transcriptionists for quality assurance is a standard practice.
While speech recognition technology offers speed and convenience, it also has limitations. The biggest disadvantage is its accuracy especially when dealing with medical terminology or background noise. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems can struggle with strong accents, fast speech, or overlapping conversations. Doctors often spend extra time reviewing and editing errors in the transcribed text. Another drawback is dependence on technology; poor internet connections or low-quality microphones can reduce performance. Compared to medical transcription, speech recognition software may save time but still requires human oversight. Many hospitals in the USA solve this by combining AI speech recognition with expert transcriptionists for better results.
Medical transcription can be illustrated when a physician captures a voice note stating, “The patient has diabetes and received insulin.” The medical transcriptionist plays that audio and drafts it in a structured medical report. This document goes into the patient’s electronic health record (EHR) system. The transcriptionist employs medical transcription software and verifies each term for correctness, grammar, and format. This results in highly accurate medical documentation that helps in the right treatment and billing process. In the USA, medical transcriptionists are indispensable in taking care of trustworthy healthcare records that comply with both clinical and legal requirements.
Industries commonly use four main types of transcription: verbatim, intelligent, edited, and medical transcription. The verbatim transcription is the transcription type that captures every sound and word including pauses and fillers. Intelligent transcripts are the transcripts from which common words and phrases have been removed, thus making them more readable and easier to understand. Edited transcription refers to the process of revising the text so that it can be used professionally. Lastly, medical transcription is the process of converting voice medical dictation into accurate reports for electronic health records (EHRs). It is a highly skilled area that requires not only a good command of medical terminology but also complete adherence to the legal standards. Medical transcription is not the same as speech recognition software; rather it is a process that includes human intervention in order to guarantee the accuracy, clarity, and context of the medical documentation in the USA health care system.
Dinesh Kumar is a healthcare workflow architect and clinical documentation expert with over a decade of real-world experience supporting physicians across multiple specialties in the United States. As the Co-Founder of ScribeMedics, he has helped transform how medical practices handle documentation, coding, and administrative workflows, reducing burnout, improving patient flow, and enabling clinicians to reclaim their day.
Since 2013, Dinesh has worked closely with providers on the front lines of patient care. Over the years, he witnessed a recurring problem: clinicians were drowning in administrative work, spending hours after clinic hours updating charts, reconciling notes, and managing documentation backlogs. Instead of accepting this as “part of the system,” he decided to fix it.
Under his leadership, ScribeMedics has grown into a global hybrid scribing and documentation support company known for accuracy, compliance, and reliable workflows. From medical scribes and CPC-certified coders to virtual back-office support, his teams help multispecialty practices increase revenue integrity, reduce charting time, and improve patient-physician satisfaction.
Dinesh works with healthcare providers, practice owners, and attorneys who want streamlined documentation, better reimbursement outcomes, and more efficient operations. His approach blends empathy, process engineering, and deep domain expertise to create systems that work, day after day.
When he isn’t optimizing clinical workflows, Dinesh mentors documentation teams, trains young professionals, and speaks about burnout prevention, workflow design, and the future of hybrid AI-driven scribing.









 Medical Transcription
Medical Transcription Medical Billing
Medical Billing Medical Coding
Medical Coding